What Is Hemodialysis and How It Works?
Healthy kidneys purify your blood and eliminate excess fluid in the form of urine. They also create compounds that are beneficial to your body's wellbeing. When your kidneys stop working, dialysis takes over some of these duties.
What is hemodialysis?
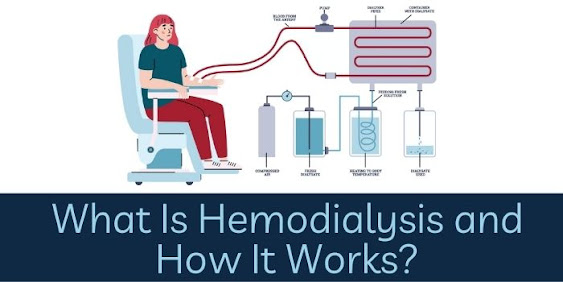
A machine takes blood from your body, filters it via a dialyzer (artificial kidney), and returns the cleansed blood to your body using hemodialysis. This 3- to 5-hour procedure takes place three times each week in a hospital or dialysis clinic.
Hemodialysis can also be performed at home. You may require at-home treatments four to seven times a week for fewer than two hours each time. You can undergo home hemodialysis at night while sleeping.
What takes place during hemodialysis?
During hemodialysis, your blood passes from your body through tubes into a dialysis machine. While in the machine, your blood passes through a filter known as a dialyzer, which cleans your blood by eliminating some of the waste and surplus fluid. The cleansed blood is then returned to your body via tubes from the dialysis machine.
Your doctor will need to create an access, or entrance, into your blood vessels in order to get your blood into the dialyzer.
How does the dialysis machine purify my blood?
The dialyzer, or filter, is divided into two parts: one for your blood and one for a cleansing solution known as dialysate. A thin membrane separates these components. Membrane carries smaller waste items in the blood, such as urea, creatinine, potassium, and surplus fluid.
Where is hemodialysis performed?
Hemodialysis can also take place at a hospital, a dialysis clinic. Based on your medical condition and preferences, you and your doctor will decide which location is ideal for you.
How long does each hemodialysis session last?
According to Hiranandani Hospital Powai News, Hemodialysis typically takes place three times a week for four hours at a time in a dialysis center. People who prefer to undergo hemodialysis at home may need to do it more frequently, 4-7 times per week for shorter periods of time each time.
Your doctor will write you a prescription that specifies how much therapy you require. According to studies, obtaining the appropriate quantity of dialysis improves your general health, keeps you out of the hospital, and allows you to live a longer life. Your dialysis care team will monitor your treatment with monthly lab tests to verify that you are receiving the appropriate quantity of dialysis, says Dr. Sujit Chatterjee, CEO of Hiranandani Hospital.
What are the risks and consequences of hemodialysis?
Some persons experience complications with the AV fistula or graft. You might have an infection, have poor blood flow, or have a blockage caused by scar tissue or a blood clot.
During dialysis, the dialysis needle seldom comes out of your arm, nor does a tube come out of the machine. A blood leak detecting device notifies you or medical personnel of the situation. This system guards against blood loss.
Conclusion
Dialysis can save a person's life if they have kidney failure or end-stage renal disease (ESRD). Hiranandani Hospital kidney transplant is also an option if you don’t want to go for dialysis. There are several forms of dialysis. Some people prefer home dialysis, while others prefer to go to a hospital or dialysis clinic. Your healthcare professional can go over dialysis choices with you to determine which therapy is best for you.

Comments
Post a Comment